Solvency (1) - Quick Ratio
|
Solvency (2) - Current Ratio
|
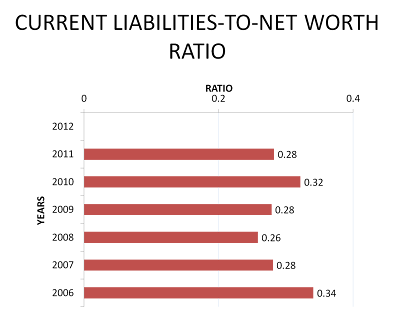
Solvency (3) - Current Liabilities to Net Worth Ratio
|
Solvency (4) - Total Liabilities to Net Worth Ratio
|
Solvency (5) - Fixed Assets to Net Worth Ratio
|
Efficiency (1) - Collection Period Ratio
|
Efficiency (2) - Net Sales to Inventory Ratio
|
Efficiency (3) - Assets to Net Sales Ratio
|
Efficiency (4) - Assets to Net Working Capital
|
Efficiency (5) - Payable to Net Sales Ratio
|
Profitability (1) - Return on Sales, or Profit Margin
|
Profitability (2) - Return on Assets
|
Profitability (3) - Return on Equity
|












No comments:
Post a Comment