Financial Statements Information - AirAsia Berhad
Financial Statements Analysis - AirAsia Berhad
Solvency (1) - Quick Ratio
- Measures the extent to which a business can cover its current liabilities with those current assets readily convertible to cash.
- Shows number of dollars of liquid assets available to cover each dollar of current debt.
- Any time the ratio is 1:1 (1.0), the business is said to be in a liquid condition.
- The larger the ratio, the greater the liquidity.
|
|
Solvency (2) - Current Ratio
- Measures the degree to which current assets cover current liabilities.
- The higher the ratio, the more likely the company will be able to meet its liabilities.
- A ratio of 2 to 1 (2.0) or higher is desirable.
|
|
Solvency (3) - Current Liabilities to Net Worth Ratio
- Indicates the amount due creditors within a year as a percentage of the owners' or stockholders' investment.
- Measures the funds creditors are risking with a business temporarily against the funds permanently invested by its owners.
- Normally a business starts to have trouble when this relationship exceeds 80%.
|
|
Solvency (4) - Total Liabilities to Net Worth Ratio
- Shows how all of the company’s debt relates to the equity of the owner or stockholders.
- The higher this ratio, the less protection there is for creditors.
- If total liabilities exceed net worth then creditors have more at stake than stockbrokers.
- The difference between this ratio and Current Liabilities to Net Worth Ratio is that it pinpoints the relative size of long-term debt, which can burden a firm with substantial interest charges.
|
|
Solvency (5) - Fixed Assets to Net Worth Ratio
- Shows the percentage of assets centered in fixed assets compared to total equity.
- Generally the higher this percentage is over 75%, the more vulnerable a concern becomes to unexpected hazards and business climate changes.
- Capital is frozen in the form of machinery and the margin for operating funds becomes too narrow to support day-to-day operations.
|
|
Efficiency (1) - Collection Period Ratio
- Helpful in analyzing the collectibility of accounts receivable, or how fast a business can increase its cash supply.
|
|
Efficiency (2) - Net Sales to Inventory Ratio
- Measures how fast inventory is moving the cash flow into the business.
- When this ratio is high, it may indicate a situation where sales are being lost because a concern is understocked and/or customers are buying elsewhere.
- If the ratio is too low, this may show that inventories are obsolete or stagnant.
|
|
Efficiency (3) - Assets to Net Sales Ratio
- Rates sales to the total investment that is used to generate those sales.
- If percentage is abnormally high, it indicates that a business is not being aggressive enough in its sales efforts, or that its assets are not being fully utilized.
- A low ratio may indicate a business is selling more than can be safely covered by its assets.
|
|
Efficiency (4) - Assets to Net Working Capital
- Measures the number of times working capital turns over annually in relation to net sales.
- Should be viewed in conjunction with the assets to sales ratio.
- A high turnover rate can indicate overtrading (excessive sales volume in relation to the investment in the business).
- A high turnover may indicate that the business relies extensively upon credit granted by suppliers or the bank as a substitute for an adequate margin of operating funds.
|
|
Efficiency (5) - Payable to Net Sales Ratio
- Measures how the company pays its suppliers in relation to the sales volume being transacted.
- A low percentage would indicate a healthy ratio. A high percentage indicates the firm may be using suppliers to help finance operations.
|
|
Profitability (1) - Return on Sales, or Profit Margin
- Measures profits after taxes on the year’s sales (profits earned per dollar of sales).
- The higher this ratio, the better prepared the business to handle downtrends brought on by adverse conditions.
|
|
Profitability (2) - Return on Assets
- The key indicator of profitability.
- A high percentage tells you the company is well run and has a healthy return on assets.
|
|
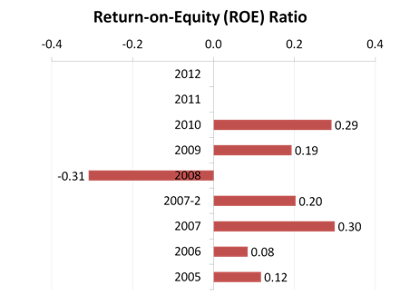
Profitability (3) - Return on Equity
- Measures the ability of a company’s management to realize an adequate return on the capital invested by the owners.
|
|
Additional Notes:
AIRASIA BERHAD
Date Announced: 27/05/2011 Annual Report 2010 (Annual Report for Financial Year Ended:31/12/2010)
Date Announced: 31/05/2010 Annual Report 2009 (Annual Report for Financial Year Ended:31/12/2009)
Date Announced: 26/06/2009 Annual Report 2008 (Annual Report for Financial Year Ended:31/12/2008)
Date Announced: 09/05/2008(
2007-2)
Annual Report 2007 (Annual Report for Financial Year Ended:31/12/2007)
Date Announced: 29/10/2007 Annual Report 2007 (Annual Report for Financial Year Ended:30/06/2007)
Date Announced: 04/12/2006 Annual Report 2006 (Annual Report for Financial Year Ended:30/06/2006)
Date Announced: 28/10/2005 Annual Report 2005 (Annual Report for Financial Year Ended:30/06/2005)























No comments:
Post a Comment